Definition
There are two instantiations of TRANSFORM. The instantiation with the rational kernel is called rat_transform and the instantiation with the floating point kernel is called transform.
An instance T of type TRANSFORM is an affine transformation of
two-dimensional space. It is given by a
3 x 3 matrix T
with
T2, 0 = T2, 1 = 0 and
T2, 2 ![]() 0 and
maps the point p with homogeneous coordinate vector
(px, py, pw) to the point T*p.
0 and
maps the point p with homogeneous coordinate vector
(px, py, pw) to the point T*p.
A matrix of the form
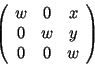
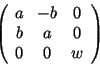
There are two instantiations: transform for the floating point kernel and rat_transform for the rational kernel.
#include < LEDA/generic/TRANSFORM.h >
Creation
| TRANSFORM | T | creates a variable introduces a variable T of type TRANSFORM. T is initialized with the identity transformation. |
| TRANSFORM | T(const INT_MATRIX t) | introduces a variable T of type TRANSFORM.
T is initialized with the matrix t.
Precondition t is a 3 x 3 matrix with t2, 0 = t2, 1 = 0 and t2, 2 |
Operations
| INT_MATRIX | T.T_matrix() | returns the transformation matrix |
| void | T.simplify() | The operation has no effect for transform. For rat_transform let g be the ggT of all matrix entries. Cancels out g. |
| RAT_TYPE | T.norm() | returns the norm of the transformation |
| TRANSFORM | T(TRANSFORM T1) | returns the transformation ToT1. |
| POINT | T(POINT p) | returns T(p). |
| VECTOR | T(VECTOR v) | returns T(v). |
| SEGMENT | T(SEGMENT s) | returns T(s). |
| LINE | T(LINE l) | returns T(l ). |
| RAY | T(RAY r) | returns T(r). |
| CIRCLE | T(CIRCLE C) | returns T(C). |
| POLYGON | T(POLYGON P) | returns T(P). |
| GEN_POLYGON | T(GEN_POLYGON P) | returns T(P). |
Non-member Functions
In any of the function below a point can be specified to the origin by replacing it by an anononymous object of type POINT, e.g., rotation90(POINT()) will generate a rotation about the origin.