Precondition: v.dim() = 2.
Definition
An instance of the data type point is a point in the two-dimensional plane R2. We use (x, y) to denote a point with first (or x-) coordinate x and second (or y-) coordinate y.
#include < LEDA/point.h >
Types
| point::coord_type | the coordinate type (double). |
| point::point_type | the point type (point). |
Creation
| point | p | introduces a variable p of type point initialized to the point (0, 0). |
| point | p(double x, double y) | introduces a variable p of type point initialized to the point (x, y). |
| point | p(vector v) | introduces a variable p of type point initialized
to the point
(v[0], v[1]).
Precondition: v.dim() = 2. |
| point | p(point p, int prec) | introduces a variable p of type point initialized
to the point with coordinates
( |
Operations
| double | p.xcoord() | returns the first coordinate of p. |
| double | p.ycoord() | returns the second coordinate of p. |
| vector | p.to_vector() | returns the vector |
| double | p.sqr_dist(point q) | returns the square of the Euclidean distance between p and q. |
| int | p.cmp_dist(point q, point r) | |
| returns
compare(p.sqr |
||
| double | p.xdist(point q) | returns the horizontal distance between p and q. |
| double | p.ydist(point q) | returns the vertical distance between p and q. |
| double | p.distance(point q) | returns the Euclidean distance between p and q. |
| double | p.distance() | returns the Euclidean distance between p and (0, 0). |
| double | p.angle(point q, point r) | returns the angle between |
| point | p.translate_by_angle(double alpha, double d) | |
| returns p translated in direction alpha by distance d. The direction is given by its angle with a right oriented horizontal ray. | ||
| point | p.translate(double dx, double dy) | |
| returns p translated by vector (dx, dy). | ||
| point | p.translate(vector v) | returns p+ v, i.e., p translated by vector
v.
Precondition v.dim() = 2. |
| point | p + vector v | returns p translated by vector v. |
| point | p - vector v | returns p translated by vector - v. |
| point | p.rotate(point q, double a) | |
| returns p rotated about q by angle a. | ||
| point | p.rotate(double a) | returns p.rotate( point(0, 0), a). |
| point | p.rotate90(point q) | returns p rotated about q by an angle of 90 degrees. |
| point | p.rotate90() | returns p.rotate90( point(0, 0)). |
| point | p.reflect(point q, point r) | |
| returns p reflected across the straight line passing through q and r. | ||
| point | p.reflect(point q) | returns p reflected across point q. |
| vector | p - q | returns the difference vector of the coordinates. |
| ostream& | ostream& O << p | writes p to output stream O. |
| istream& | istream& I >> point& p | reads the coordinates of p (two double numbers) from input stream I. |
Non-Member Functions
| int | cmp_distances(point p1, point p2, point p3, point p4) | |
| compares the distances (p1,p2) and (p3,p4). Returns +1 (-1) if distance (p1,p2) is larger (smaller) than distance (p3,p4), otherwise 0. | ||
| point | center(point a, point b) | returns the center of a and b, i.e.
a + |
| point | midpoint(point a, point b) | |
| returns the center of a and b. | ||
| int | orientation(point a, point b, point c) | |
| computes the orientation of points a, b, and c as
the sign of the determinant
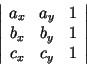
i.e., it returns +1 if point c lies left of the directed line through a and b, 0 if a,b, and c are collinear, and -1 otherwise. |
||
| int | cmp_signed_dist(point a, point b, point c, point d) | |
| compares (signed) distances of c and d to the straight line passing through a and b (directed from a to b). Returns +1 (-1)if c has larger (smaller) distance than d and 0 if distances are equal. | ||
| double | area(point a, point b, point c) | |
| computes the signed area of the triangle determined by a,b,c, positive if orientation(a, b, c) > 0 and negative otherwise. | ||
| bool | collinear(point a, point b, point c) | |
| returns true if points a, b, c are collinear, i.e., orientation(a, b, c) = 0, and false otherwise. | ||
| bool | right_turn(point a, point b, point c) | |
| returns true if points a, b, c form a righ turn, i.e., orientation(a, b, c) > 0, and false otherwise. | ||
| bool | left_turn(point a, point b, point c) | |
| returns true if points a, b, c form a left turn, i.e., orientation(a, b, c) < 0, and false otherwise. | ||
| int | side_of_halfspace(point a, point b, point c) | |
| returns the sign of the scalar product
(b - a)*(c - a). If
b |
||
| int | side_of_circle(point a, point b, point c, point d) | |
| returns +1 if point d lies left of the directed circle through points a, b, and c, 0 if a,b,c,and d are cocircular, and -1 otherwise. | ||
| bool | incircle(point a, point b, point c, point d) | |
| returns true if point d lies in the interior of the circle through points a, b, and c, and false otherwise. | ||
| bool | outcircle(point a, point b, point c, point d) | |
| returns true if point d lies outside of the circle through points a, b, and c, and false otherwise. | ||
| bool | cocircular(point a, point b, point c, point d) | |
| returns true if points a, b, c, and d are corcircular. | ||
| bool | affinely_independent(array<point> A) | |
| decides whether the points in A are affinely independent. | ||
| bool | contained_in_simplex(array<point> A, point p) | |
| determines whether p is contained in the simplex spanned
by the points in A. A may consists of up to 3
points.
Precondition The points in A are affinely independent. |
||
| bool | contained_in_affine_hull(array<point> A, point p) | |
| determines whether p is contained in the affine hull of the points in A. | ||