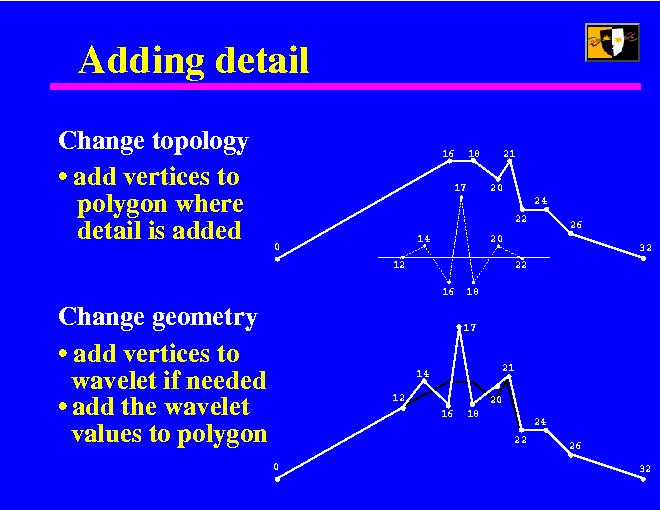
Let's see how we can add detail, that is, wavelet coefficients, to a model.
The picture on the top represents our current one-dimensional polyline. We intend to add to it a wavelet centered on vertex 17. This particular wavelet has nonzero support between the vertices 12 and 22, so it should only change the model within that segment.
First we change the model topology by adding all wavelet vertices that don't already exist in the model. In the example, that would be 12, 14, and 17. Then, if the model contains some vertices within the support of the wavelet that don't appear in the wavelet, we add them to it (only vertex 21).
Now we change the model geometry by adding the values at the wavelet vertices to the corresponding vertices in the model. For example, vertex 12 stays put, it is only used to separate the influence of the wavelet from the rest of the model, vertex 14 moves up a bit, 16 moves down, and so forth.
As I said, this example shows a one-dimensional example. For a 2D polygon, the topology changing part (that is, adding of vertices) is the same. For the geometry changing part, we simply have separate coefficients for the x and y coordinates.