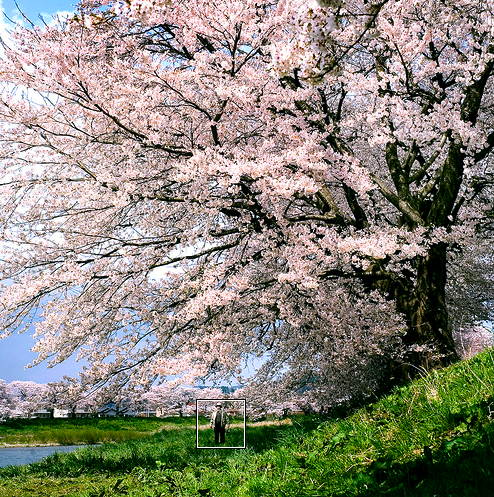
Project Proposal : Sakura ("Cherry Blossom")
Team
- Tom Wang
- Priscilla Pham
Images
- Some ideas of the image we will attempt to physically render are the following:
|
|
|
|
Overview
- Sakura trees (also known as cherry blossom trees) are among the most beautiful trees in nature and also present a worthwhile rendering challenge. We hope to capture the beauty of the sakura tree by procedurally generating a realistic texture for the bark of the tree [1] and procedurally modeling the branch generation of the tree using a 3D L-system [2]. In addition, we will procedurally model blossom petals by using an adaptation of the rose curve. Finally, we intend to employ subsurface scattering on the petals to capture the realistic details of softness and faint translucency.
3D L-System
Background
- An L-system is a parallel string rewriting system, in which a simulation begins with an initial string called the axiom, which consists of modules, or symbols with associated numerical parameters. In each step of the simulation, rewriting rules—or productions—replace all modules in the predecessor string by successor modules. The resulting string can be visualized as a series of commands that link nodes, represent rotations, and distances between nodes.
Tree Rendering
- In the context of procedural tree branch generation, an L-system can be defined as a series of generated cylinders of varying 3D orientation, thickness, and length. Since the L-system defines a particular grammar for branch generation, we will fine-tune the grammar and production rules of our 3D L-system to match the cherry blossom tree species. In addition, we will introduce probability models based on observations in nature (number of branches from a sakura tree, depth of branching) to match randomness in nature. With more time, we would like to enhance the branch models to be more advanced with general cylinders.
- We would like to emulate the biological properties of cherry blossom trees and will study real trees in nature to create a probability distribution function of branching possibilities (define angles in 3D as well as lengths) that best mimics real trees. This PDF will be defined as a normal distribution over a series of parameters varying by depth of branching (trunk is thicker and longer than a final leaf branch). Finally, the PDF will be species specific (a weeping willow, for example, has branches that point down, whereas a sakura tree demonstrates little if any negative Z-axis rotation).
- An example of a simple implementation is the following image:
Tree Design Evolution
Basic Texture, No Branching
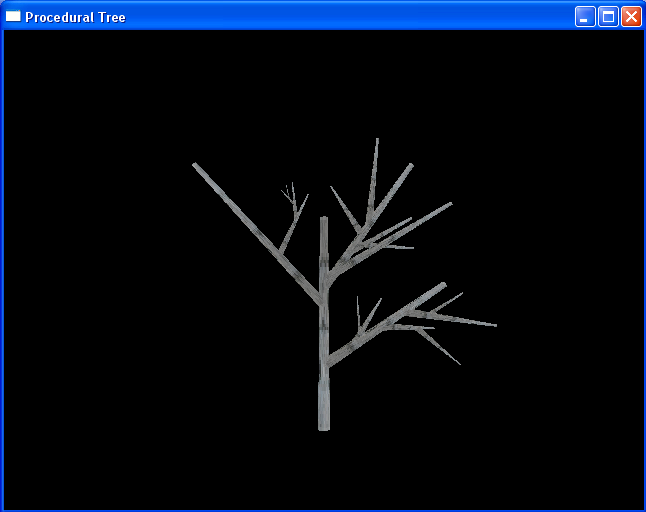
Basic Branching, Lighting

Model Leaves, Perspective

True Branching, Cherry Tree Properties
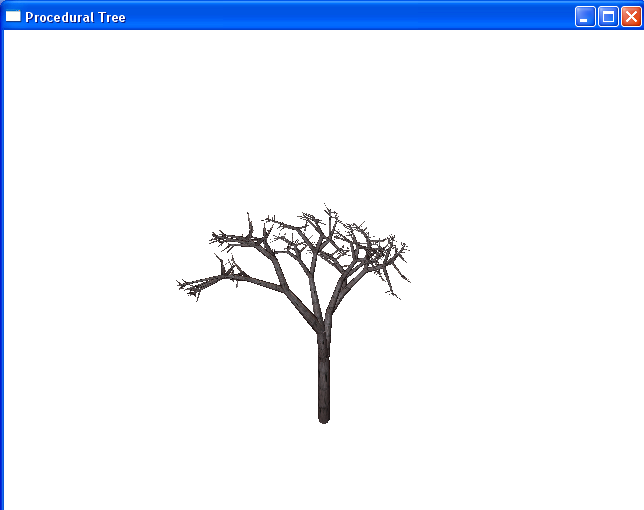
Gnarled Rotations, Proportional Trunk

Smooth Gnarled, Reduce Leaf Noise

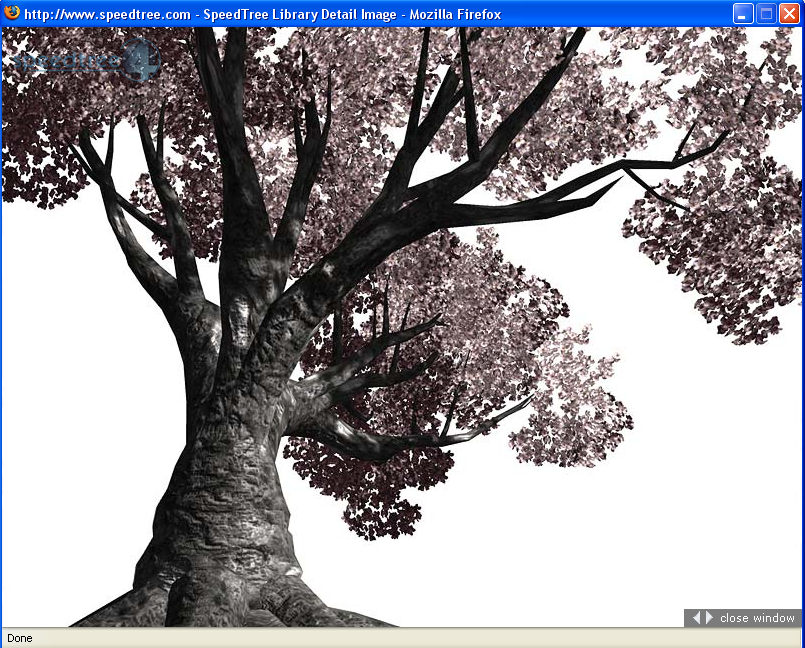
SpeedTree Implementation (for reference)
Procedural Bark
Texture Generation
- Creating a bark texture as stated in [1] involves a complex series of equations dictating when and where fractures occur in bark given a particular length of a strip of bark. By combining these strips of bark and solving the fracture equations over a series of strips, we can combine these strips to generate a texture map. The fracture equations contain an innate variation law that allows for randomness in generation.
- After the fractures are generated, we overlay with a bump mapped bark texture to provide enhanced detail.
- However, the implementation in [1] works best for "fracture bark" trees whereas the cherry blossom tree has "lenticel bark" type. This means that we will need to extend the implementation in [1] from vertical fractures to horizontal fractures or will need to create procedural texture maps representing horizontal rather than vertical noise.
- The bark of a cherry blossom tree looks like:

Texture Mapping
- After tree generation has concluded, we map coordinates from cylinders of branches directly onto texture coordinates of the procedural bark texture. With more time, we'd like to implement the mesh mapping strategy from [1] to ensure that fractures line up at branch junctions. However, given the scene complexity that we hope to achieve with blossom petals, such additional bark complexity may prove infeasible and not valuable.
Classic Plane Curves
Background
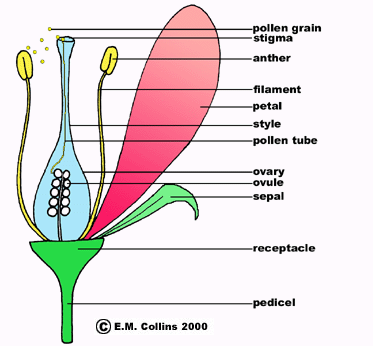
Prunus serrulata are dicots and posses five petals, five sepals, several stamen and a pistil.
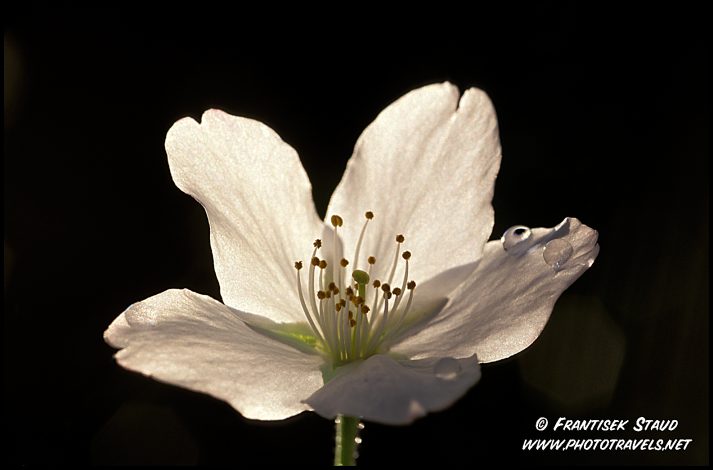

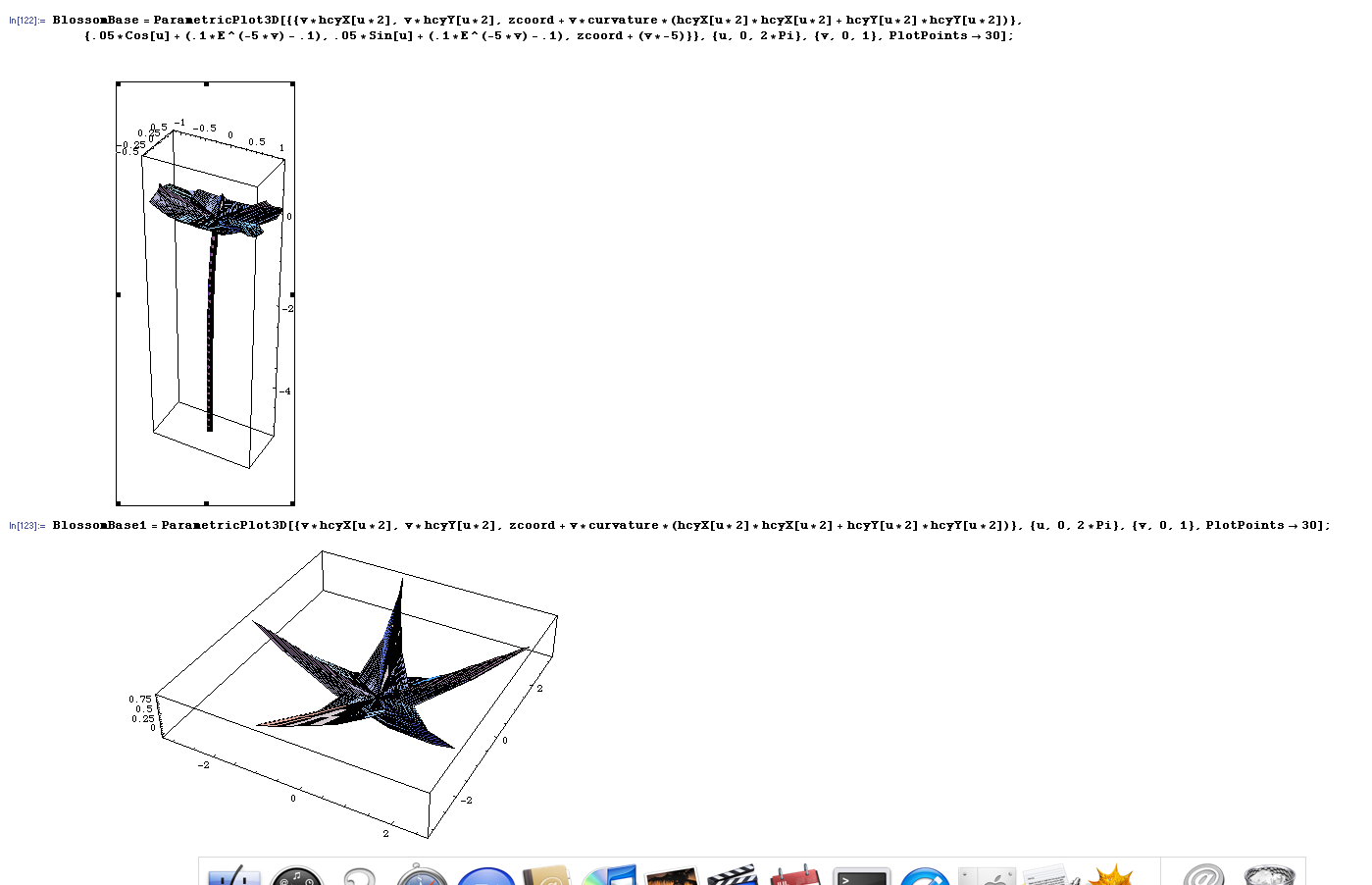
We observed that in this case that the beauty of nature coincides with the beauty of mathematics. More specifically, the shape and geometry of these blossoms can be recreated with curves defined in polar coordinates.
Blossom Rendering
We will choose curves that most closely resemble the shapes of most importantly the petals and sepals. Here is a diagram of the parts of a typical dicot:
What currently looks like the best choices are the cardioid
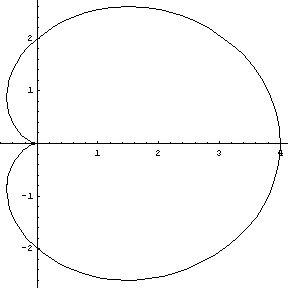
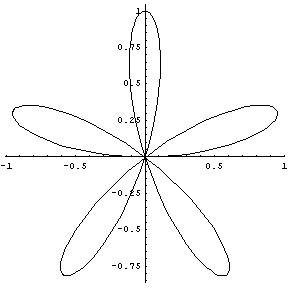
or the 5 petal rose curve for the petals

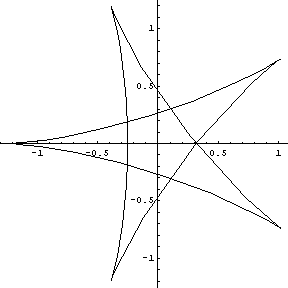
and the 5 point hypercycloid for the sepals.
All petals together:

The petals are cardioids with the z-coordinate following the shape of a paraboloid to create the upcurving effect of the petals. The position of the petals around the center of the blossom are calculated according to those of the 5 petal rose curve.
In addition we will use sin/cosine curves with noise in the z-plane so that the petals are not completely flat and emulate the imperfection in nature. The pistil and stamen are relatively straightforward to generate, as they are just segments with ellipsoids at the end.

Texture Mapping
After petal generation has concluded, we plan to generate randomized veins on the petal (all originating from the center) with a jitter transform. We will look more into multijugate/whorled phyllotaxis and research how the macro structure of the petal can relate to the cellular texture of the petals to generate the petal texture.
Subsurface Scattering
Subsurface scattering (or SSS) is a mechanism of light transport in which light penetrates the surface of a translucent object, is scattered by interacting with the material, and exits the surface at a different point. The light will generally penetrate the surface and be reflected a number of times at irregular angles inside the material, before passing back out of the material at an angle other than the angle it would reflect at had it reflected directly off the surface. (Wikipedia)
Background
Rose petals are translucent and to achieve the realistic, silky, lifelike softness we must implement SSS. This may be achieved with the reflection model described in the paper by Hanrahan/Krueger. We will also study the structure and cellular layers of petals. So far, we have learned that two especially characteristic layers, such as upper epidermal cells which are dome-shaped and spongy cells which reflect much light, cause the unique appearance of rose petals.
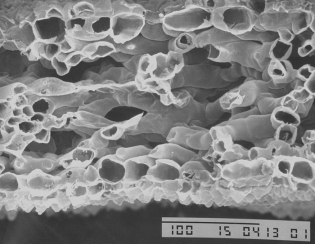
- Petals resemble thin surfaces, and their cross-sections can be described by open contours. We hope to apply this and other plant biology knowledge to enhance the appearance of the sakura petals.
Petal SSS
We will, amongst other things, need to modify the Monte Carlo integrator code. We are planning to implement SSS as described in the Hanrahan/Krueger paper, adapting the layers to the tissue structure of our blossoms. We will calcuate the radiance by summing the radiance from surface and subsurface scattering, and the transmitted radiance from the sum of the radiance from absorption and subsurface scattering. From these values we calculate the BRDF and the BTDF and take into account the Fresnel coefficients. Since the petals are very thin, we will experiment first with single layer SSS, but if the desired results cannot be achieved from this we will continue adapt our algorithms according to what we found out from studying the cellular structure of flower petals.
Links
[1] Synthetic Bark
[2] Procedural Multiresolution for Plant and Tree Rendering
[4] Reflection from Layered Surfaces due to Subsurface Scattering [5] Deborah R. Fowler, Przemyslaw Prusinkiewicz, and Johannes Battjes. A Collision-based Model of Spiral Phyllotaxis. Proceedings of SIGGRAPH '92 (Chicago, Illinois, July 26-31, 1992), In Computer Graphics, 26, 2, (July 1992), ACM SIGGRAPH, New York, pp. 361-368.