The class Halfedge_data_structure_decorator<HDS> provides additional functions to examine and to modify a halfedge data structure. All these functions take care of the different capabilities a certain halfedge data structure may have or may not have. The functions evaluate the support type tags of the halfedge data structure to decide on the actions. If the feature is not supported nothing is done. Note that for example the creation of new halfedges is mandatory for all halfedge data structures and will not appear here again.
#include <CGAL/Halfedge_data_structure_decorator.h>
|
| |
|
the type of the halfedge data structure.
| |
|
| |
|
the vertex type of the halfedge data structure.
| |
|
| |
|
the halfedge type of the halfedge data structure.
| |
|
| |
|
the facet type of the halfedge data structure.
| |
|
| |
|
the point type used in the vertex if
points are supported.
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
| returns the incident halfedge of if supported, NULL otherwise. | ||
|
|
| |
| returns the incident vertex of if supported, NULL otherwise. | ||
|
|
| |
| returns the previous halfedge of if supported, NULL otherwise. | ||
|
|
| |
| returns the previous halfedge of . Uses the prev() method if supported or performs a search around the facet using next(). | ||
|
|
| |
| returns the incident facet of if supported, NULL otherwise. | ||
|
|
| |
| returns the incident halfedge of if supported, NULL otherwise. | ||
|
|
| |
| returns a new vertex from hds if vertices are supported, NULL otherwise. | ||
|
|
| |
| returns a copy of from hds if vertices are supported, NULL otherwise. | ||
|
|
| |
| returns a new vertex from hds initialized to if vertices and points are supported, NULL otherwise. | ||
|
|
| |
| returns a new facet from poly if facets are supported, NULL otherwise. | ||
|
|
| |
| returns a copy of from hds if facets are supported, NULL otherwise. | ||
|
|
| |
| returns a halfedge from a newly created loop in hds consisting of a single closed edge, one vertex and two facets (if supported respectively). | ||
|
|
| |
| returns a halfedge from a newly created segment in hds consisting of a single open edge, two vertices and one facet (if supported respectively). | ||
|
|
| |
| removes the vertex if vertices are supported. | ||
|
|
| |
| removes the facet if facets are supported. | ||
|
|
| |
|
removes the
facet incident to h from hds and changes all halfedges
incident to the facet into border edges or removes them from the
hds if they were already border edges, i.e. if there remains no
facet incident to this edge after removing the facet. See
make_hole(h) for a more specialized variant. Precondition: h != NULL. If facets are supported, Supports_removal must be equivalent to Tag_true. | ||
|
|
| |
|
removes the vertices, halfedges, and facets that belong to the
connected component of . Precondition: Supports_removal must be equivalent to Tag_true. For all halfedges in the connected component g.next() != NULL. | ||
|
|
| |
| makes h->opposite() the successor of . | ||
|
|
| |
| makes h->opposite() the successor of and sets the incident vertex of to . | ||
|
|
| |
| inserts the tip of the edge into the halfedges around the vertex pointed to by . Halfedge h->opposite() is the new successor of and h->next() will be set to v->next(). The vertex of will be the one points to if vertices are supported. | ||
|
|
| |
| removes the edge h->next()->opposite() from the halfedge cycle around the vertex pointed to by . The new successor halfedge of will be h->next()->opposite()->next(). | ||
|
|
| |
| inserts the halfedge between and f->next(). The facet of will be the one points to if facets are supported. | ||
|
|
| |
| removes edge h->next() from the halfedge cycle around the facet pointed to by . The new successor of will be h->next()->next(). | ||
|
|
| |
|
loops around the vertex incident to and sets all vertex
pointers to . Precondition: h != NULL. | ||
|
|
| |
|
loops around the facet incident to and sets all facet
pointers to . Precondition: h != NULL. | ||
|
|
| |
|
performs an edge flip, i.e. Delaunay flip. It returns after
rotating the edge one vertex in the direction the facet
orientation points to. Precondition: h != NULL and the facet cycles on both sides of are triangles. | ||
|
|
| |||
|
removes the facet incident to h from hds and creates a hole. Precondition: h != NULL and !(h->is_border()). If facets are supported, Supports_removal must be equivalent to Tag_true. | ||||
|
|
| |||
|
creates a new facet from hds and fills the hole incident to h. Precondition: h != NULL and h->is_border(). | ||||
|
|
| |||
|
creates a new facet from hds within the hole incident to
and by connecting the tip of with the tip of
with a new halfedge from hds and filling this separated part
of the hole with a new facet from hds, such that the new
facet is incident to . Returns the halfedge of the new edge that
is incident to the new facet. Precondition: h != NULL, g != NULL, h->is_border(), g->is_border() and can be reached along the same hole starting with . | ||||
The following Euler operations modify consistently the combinatorial structure of the halfedge data structure. The geometry remains unchanged. Note that well known graph operations are also captured with these Euler operators, for example an edge contraction is equal to an join_vertex() operation, or an edge removal to join_facet().
Given a halfedge data structure hds and a halfedge pointer four special applications of the Euler operators are: split_vertex(h,h) results in an antenna emanating from the tip of h. split_vertex(h,h->next()->opposite()) results in an edge split of the halfedge h->next with a new vertex in-between. split_facet(h,h) results in a loop directly following h. split_facet(h,h->next()) results in a bridge parallel to the halfedge h->next with a new facet in-between.

|
|
| |
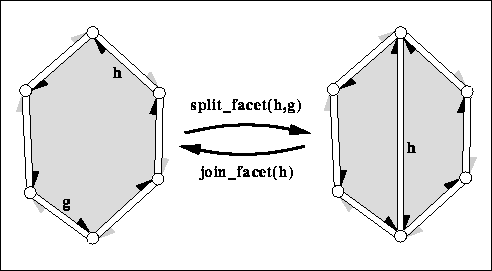
|
splits the facet incident to h and g into two facets
with a new diagonal between the two vertices denoted by h and
g respectively. The second (new) facet obtained from
hds is a copy of the first facet. The new diagonal is
returned. The time is proportional to the distance from h
to g around the facet. Precondition: g must be reachable from h around the facet. | ||
|
|
| |
|
joins the two facets incident to . The facet incident to
h->opposite() gets removed by hds. Both facets might be
holes. Returns the predecessor of around the facet. The invariant
join_facet( split_facet( h, g)) returns and keeps
the data structure unchanged. The time is proportional to the size
of the facet removed and the time to compute h->prev(). Precondition: HDS supports removal of halfedges and facets. | ||
|
|
| |
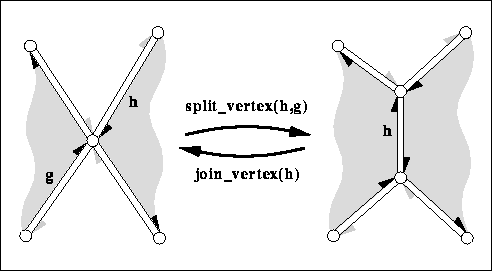
|
splits the vertex incident to h and g into two vertices
and connects them with a new edge. The second (new) vertex
obtained from hds is a copy of the first vertex. The
new edge is returned. The time is proportional to the distance
from h to g around the vertex. Precondition: g must be reachable from h around the vertex. | ||
|
|
| |
|
joins the two vertices incident to . The vertex denoted by
h->opposite() gets removed by hds. Returns the predecessor of
around the vertex. The invariant
join_vertex( split_vertex( h, g)) returns
and keeps hds unchanged.
The time is proportional to the degree of the vertex removed and
the time to compute h->prev(). Precondition: HDS supports removal of vertices and halfedges. | ||
|
|
| |||
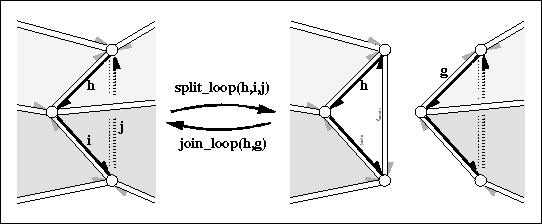
|
cuts the halfedge data structure into two parts along the cycle .
Three new vertices (one copy for each vertex in the cycle) and
three new halfedges (one copy for each halfedge in the cycle), and
two new triangles will be
created. will be incident to the first new triangle.
The return value will be a halfedge denoting the
new halfedge of the second new triangle which was h-opposite()
beforehand. Precondition: are distinct, consecutive vertices of the halfedge data structure and form a cycle: i.e. h->vertex() == i->opposite()->vertex(), ..., j->vertex() == h->opposite()->vertex(). | ||||
|
|
| |||
|
glues the boundary of two facets together.
Both facets and the vertices of the facet loop gets removed.
Returns . Both facets might be holes.
The invariant join_loop( h, split_loop( h, i, j))
returns and keeps the data structure unchanged. Precondition: HDS supports removal of vertices, halfedges, and facets. The facets denoted by and are different and have an equal degree (i.e. number of edges). | ||||
|
|
| |
| sets the point of to . | ||
|
|
| |
| sets the point of the vertex incident to to . | ||
|
|
| |
| sets the incident halfedge of to . | ||
|
|
| |
| sets the incident halfedge of the vertex incident to to . | ||
|
|
| |
| sets the incident vertex of to . | ||
|
|
| |
| sets the previous link of to . | ||
|
|
| |
| sets the incident facet of to . | ||
|
|
| |
| sets the incident halfedge of to . | ||
|
|
| |
| sets the incident halfedge of the facet incident to to . | ||
|
|
| |||
|
returns true if the halfedge data structure hds is
valid with respect to the level value. If verbose is
true, statistics are printed to cerr. A halfedge data
structure has no definition of validness of its own, but a useful
set of tests is defined with the following levels: Level 0: The number of halfedges is even. All pointers except the facet pointer for border halfedges are unequal to NULL. For all halfedges : The opposite halfedge is different from and the opposite of the opposite is equal to . The next of the previous halfedge is equal to . For all vertices : the incident vertex of the incident halfedge of is equal to . The halfedges around starting with the incident halfedge of form a cycle. For all facets : the incident facet of the incident halfedge of is equal to . The halfedges around starting with the incident halfedge of form a cycle. Some checks that redundancies among internal variables holds, e.g. that the iterators enumerate as many items as the related size value indicates. Level 1: All tests of level 0. For all halfedges : The incident vertex of is equal to the incident vertex of the opposite of the next halfedge. The incident facet of is equal to the incident facet of the next halfedge. Level 2: All tests of level 1. The sum of all halfedges that can be reached through the vertices must be equal to the number of all halfedges, i.e. all halfedges incident to a vertex must form a single cycle. Level 3: All tests of level 2. The sum of all halfedges that can be reached through the facets must be equal to the number of all halfedges, i.e. all halfedges surrounding a facet must form a single cycle (no holes in facets). Level 4: All tests of level 3 and normalized_border_is_valid. | ||||
|
|
| |||
| returns true if the border halfedges are in normalized representation, which is when enumerating all halfedges with the iterator: The non-border edges precede the border edges. For border edges, the second halfedge is a border halfedge. (The first halfedge may or may not be a border halfedge.) The halfedge iterator border_halfedges_begin() denotes the first border edge. If verbose is true, statistics are printed to cerr. | ||||