Yangyan Li, Xiaokun Wu, Yiorgos Chrysanthou, Andrei Sharf, Daniel Cohen-Or, Niloy J. Mitra
ACM SIGGRAPH 2011
Abstract:
Given a noisy and incomplete point set, we introduce a method that
simultaneously recovers a set of locally fitted primitives along with
their global mutual relations. We operate under the assumption that
the data corresponds to a man-made engineering object consisting
of basic primitives, possibly repeated and globally aligned under
common relations. We introduce an algorithm to directly couple the
local and global aspects of the problem. The local fit of the model is
determined by how well the inferred model agrees to the observed
data, while the global relations are iteratively learned and enforced
through a constrained optimization. Starting with a set of initial
RANSAC based locally fitted primitives, relations across the primitives
such as orientation, placement, and equality are progressively
learned and conformed to. In each stage, a set of feasible relations
are extracted among the candidate relations, and then aligned to,
while best fitting to the input data. The global coupling corrects the
primitives obtained in the local RANSAC stage, and brings them to
precise global alignment. We test the robustness of our algorithm on
a range of synthesized and scanned data, with varying amounts of
noise, outliers, and non-uniform sampling, and validate the results
against ground truth, where available.
Results:
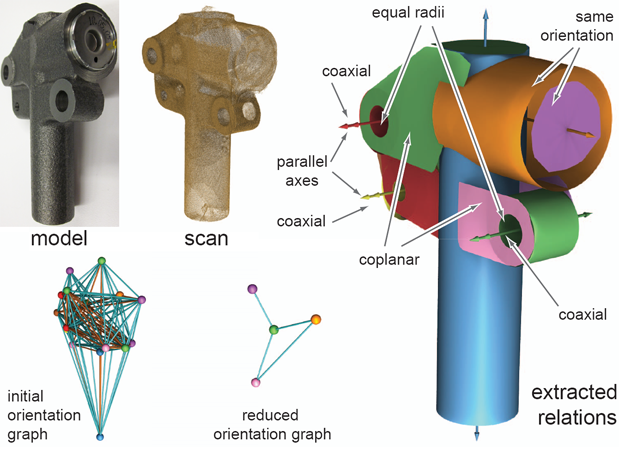
| (Right) Starting from a noisy scan, our algorithm recovers the
primitive faces along with their global mutual relations, when are
then used to produce a final model (all lengths in mm). |
|
 |
|
| |
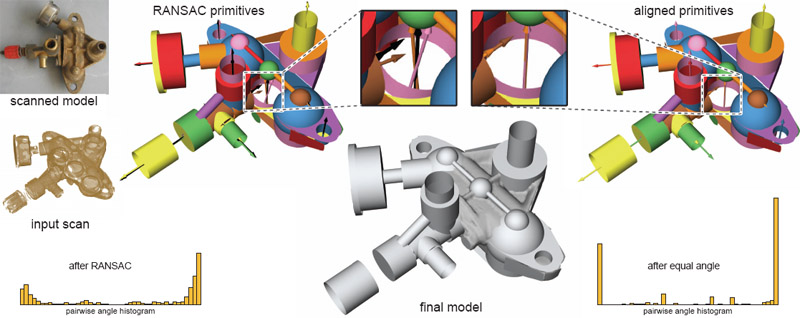
| (Bottom) Cylinder, plane, and sphere primitives are aligned using extracted coaxis, coplanar, parallel/orthogonal axes, equal angle as well
as equal length constraints. They converge to the final model after two iterations of RANSAC fitting and constraint optimization. We overlap
the final result on the initial RANSAC results for comparison; the histograms demonstrate the effect in the primitive pair angle space. |
 |
 |
|
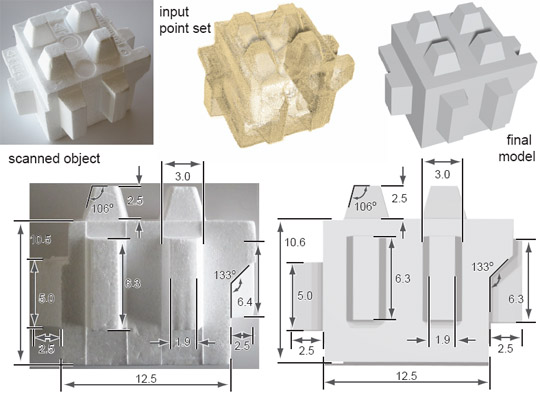
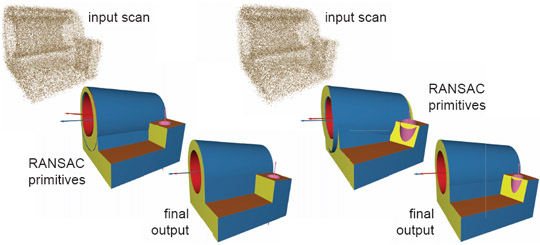
(Left) Starting from a noisy scan, our algorithm recovers the
primitive faces along with their global mutual relations, when are
then used to produce a final model (all lengths in mm). |
|
| |
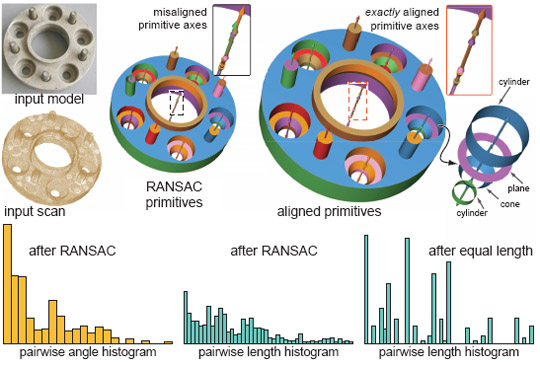
| (Right) Aligning to global relations corrects for significant
misaligned RANSAC primitives obtained using local fits. However,
when the data quality is sufficiently poor, our algorithm may
fail to recover all global relations, and hence the reconstruction is
only partially correct. |
|
 |
|
| |
Acknowledgements:
We are grateful to Ruwen Schnabel for making code from [Schnabel
et al. 2007] publicly available, Ran Gal and Suhib Alsisan for
proofreading the paper, KAUST car garage for lending machine
parts for scanning, and AIM@Shape for the joint model. Niloy thanks Tanveer Alam for
initial experiments for this project; Pierre Alliez, Cengiz Oztireli for
running comparison tests using their state-of-the-art reconstruction
algorithms; and Reinhard Klein for inspiring discussions.
Bibtex:
@article{li_globFit_sigg11,
AUTHOR = "Yangyan Li and Xiaokun Wu and Yiorgos Chrysanthou and Andrei Sharf and Daniel Cohen-Or and Niloy J. Mitra",
TITLE = "GlobFit: Consistently Fitting Primitives by Discovering Global Relations",
JOURNAL = "ACM Transactions on Graphics",
VOLUME = "30",
NUMBER = "4",
PAGES = "to appear",
YEAR = "2011",
}