Assignment 4
Part 2
Question 1
p(phi,theta) = 1/pi * cos(theta) * sin(theta)
Part 3
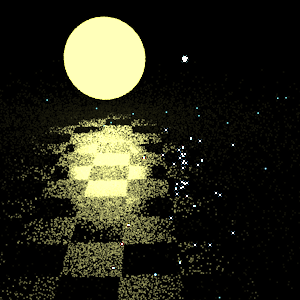
BSDF-only Sampling |
Light-only Sampling |
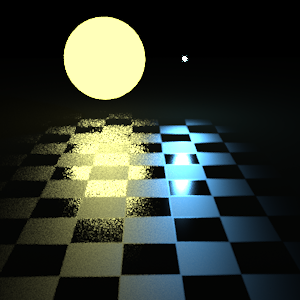
Multi-Importance Sampling |
|
|
|
Question 2
There is less noise in regions of the floor where the specular highlight is very likely to reflect the yellow light source. Since the yellow light source is very large, in the area of floor where specular rays tend to reflect towards the yellow light, these rays are quite likely to intersect the yellow light. It's reflection is therefore consistently visible and noise is low.
The area of the floor whose specular highlight is very likely to reflect the blue light, however, has severe noise. Because the blue light is very small, few rays which reflect towards it actually intersect it and the blue light's reflection appears in few samples.
Question 3
When sampling only the light source in this scene, the worst case noise from the bsdf-only render becomes the best case and the best case from the bsdf-only render becomes the worst case.
The blue light's reflection, which formerly appeared as sparse noise, looks nearly perfect. Since the light is quite physically small, consecutive sample rays strike at similar locations and give extremely consistent results.
However, the yellow light's reflection is fairly noisy due to the large surface area being sampled over. The variance of angle and distance between consecutive sample rays is large enough to show significant noise.
Question 4
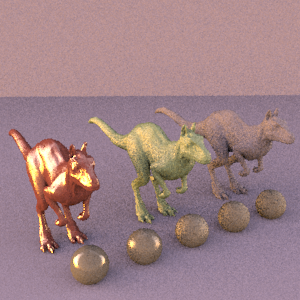
Jack Sprat could eat no fat. His wife could eat no lean. Likewise, the look of our platter when we sample solely according to the light source or the BSDF. However, bring the two sampling techniques together and they complement one another well; a proper blend of their results will produce more desirable, statistically unbiased, results.
The improved results are due not only to blending, but also because of the weight applied to each according to its "quality" in light of the heuristic used to obtain it. This quality can be roughly explained as:
Given: - a sample - the heuristic which produced this sample - and all other heuristics we are using to produce samples What is the probability that this particular heuristic would have produced this particular sample over all possible heuristics which could have produced it?
By weighting our results in such a fashion, we downplay the importance of samples whose existence is not statistically probable. This alleviates the far-spread noise seen in the bsdf-only render. Here, several statistically unlikely rays were produced which succeeded in striking the blue light, creating bright points far afield of where one would expect. In multi-importance sampling, these rays are seen as far less likely to have been produced by the bsdf than by simply sampling the light from this point, and we weight down the errant bsdf-produced rays accordingly.
Part 4
Question 5
Environment Map |
||
|
||
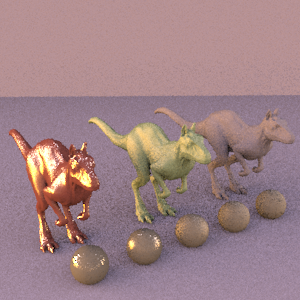
BSDF-only Sampling |
Light-only Sampling |
Multi-Importance Sampling |
|
|
|
It is in the regions of specular highlight that the bsdf-sampled image really shines. When the eye ray glances specular surfaces at low angles, the Sample_f for reflection rays tends to send them in a fairly uniform direction. This leads to little variance, from one sample to the next, in the location sampled on the environment map and, hence, very little noise.
Overall, however, the bsdf-sampled image is extremely noisy. The noise is most pronounced on less specular objects and the areas on specular objects where a specular highlight is not present. Here, there is less favor to the direction of reflection, leading to reflection rays with greater variation in direction. These scattered reflection rays end up sampling widely within areas of high frequency in the environment map, resulting in high frequency noise in areas of low specularity.
Question 6
Sampling solely according to luminance leads to less noise because samples are drawn primarily from the bright areas of the environment map. The high frequency changes in the environment map occur when it transitions from areas of dark to bright. Since the dark areas are seldom sampled in this lighting scheme, the variance we experience is primarily exposed to the low frequency changes within the bright spots. Though high frequency changes exist, we seldom sample across them.
This contrasts with the bsdf-samples which scatters rays within a areas of the environment without regard to their luminance. We frequently sample across high frequency noise, from dark to light, and the result is a noisy image.
Environment Map |
||
|
||
BSDF-only Sampling |
Light-only Sampling |
Multi-Importance Sampling |
|
|
|
The sunset environment has very little noise whether sampled according to luminance or the bsdf. This is because the environment map is composed almost entirely of low frequency changes. Thus, whether sampling according to luminance, or directionality, there are few high frequency changes to contribute noise.
Question 7
An environment map with high frequency changes in color, yet the same luminance everywhere, would look better using cosine-weighted sampling. Since the environment map has the same luminance everywhere, samples would be drawn equally over all parts of the map from any given point in the world. Using the cosine-weighted strategy, however, samples would be drawn primarily from the portions of the environment map most directly shining upon the surface point. The luminance weighted image would blur the colors significantly, especially in specular highlights, while the cosine-weighted image would show sharper, more accurate shifts in color.
Environment Map |
|
Light-only Sampling |
|
I attempted to create such an environment map but did not get the kind of noise I was expecting. I suppose colors of the same luminance are similar enough that, when blurred together, it's tough to tell much of a difference. Still, the cosine weighted image would likely have less noise.
Question 8
Environment Map |
||
|
||
BSDF-only Sampling |
Light-only Sampling |
Multi-Importance Sampling |
|
|
|
Environment Map |
||
|
||
BSDF-only Sampling |
Light-only Sampling |
Multi-Importance Sampling |
|
|
|
The images don't look all that much different to me compared with their counterparts in view 1 when using the sunset environment map. As it did in view 1, the map's low frequency texture leads to little noise.
When using the grace environment map, however, the bodies of the killeroos do look more similar to one another in view 2 than view 1. This is due to the lack of visible specular highlights. It seems, at this angle, that far few reflection rays aim into bright portions of the environment map. It was these specular highlights in view 1 that made the first killeroo look so much different from the others. Without these highlights, the bsdf sampled rays behave quite similarly across all killeroos. Likewise, the light-sampled rays bounce back to the eye with similar bsdf pdfs across all killeroos.