| int |
L.length() |
returns the length of L.
|
| int |
L.size() |
returns L.length().
|
| bool |
L.empty() |
returns true if L is empty, false otherwise.
|
| list_item |
L.first() |
returns the first item of L (nil if L is empty).
|
| list_item |
L.last() |
returns the last item of L. (nil if L is empty)
|
| list_item |
L.get_item(int i) |
returns the item at position i (the first position is 0).
Precondition
0 < = i < L.length(). Note that this takes
time linear in i.
|
| list_item |
L.succ(list_item it) |
returns the successor item of item it, nil if
it = L.last().
Precondition it is an item in L.
|
| list_item |
L.pred(list_item it) |
returns the predecessor item of item it, nil if
it = L.first().
Precondition it is an item in L.
|
| list_item |
L.cyclic_succ(list_item it) |
| |
|
returns the cyclic successor of item it, i.e.,
L.first() if it = L.last(), L.succ(it) otherwise.
|
| list_item |
L.cyclic_pred(list_item it) |
| |
|
returns the cyclic predecessor of item it, i.e,
L.last() if it = L.first(), L.pred(it) otherwise.
|
| E |
L.contents(list_item it) |
returns the contents L[it] of item it.
Precondition it is an item in L.
|
| E |
L.inf(list_item it) |
returns L.contents(it).
|
| E |
L.front() |
returns the first element of L, i.e. the contents
of L.first().
Precondition L is not empty.
|
| E |
L.head() |
same as L.front().
|
| E |
L.back() |
returns the last element of L, i.e. the contents
of L.last().
Precondition L is not empty.
|
| E |
L.tail() |
same as L.back().
|
| int |
L.rank(E x) |
returns the rank of x in L, i.e. its first
position in L as an integer from [1...| L|]
(0 if x is not in L). Note that this takes
time linear in rank(x). Precondition compare has to be
defined for type E.
|
| list_item |
L.push(E x) |
adds a new item < x > at the front of L and
returns it (L.insert(x,L.first(),LEDA::before)).
|
| list_item |
L.push_front(E x) |
same as L.push(x).
|
| list_item |
L.append(E x) |
appends a new item < x > to L and returns
it (L.insert(x,L.last(),LEDA::after)).
|
| list_item |
L.push_back(E x) |
same as L.append(x).
|
| list_item |
L.insert(E x, list_item pos, int dir=LEDA::after) |
| |
|
inserts a new item < x > after (if dir=LEDA::after)
or before (if dir=LEDA::before) item pos into L and
returns it (here LEDA::after and LEDA::before
are predefined constants).
Precondition it is an item in L.
|
| E |
L.pop() |
deletes the first item from L and returns its contents.
Precondition L is not empty.
|
| E |
L.pop_front() |
same as L.pop().
|
| E |
L.Pop() |
deletes the last item from L and returns its contents.
Precondition L is not empty.
|
| E |
L.pop_back() |
same as L.Pop().
|
| E |
L.del_item(list_item it) |
deletes the item it from L and returns its contents L[it].
Precondition it is an item in L.
|
| E |
L.del(list_item it) |
same as L.del_item(it).
|
| void |
L.erase(list_item it) |
deletes the item it from L.
Precondition it is an item in L.
|
| void |
L.remove(E x) |
removes all items with contents x from L.
Precondition compare has to be defined for type E.
|
| void |
L.move_to_front(list_item it) |
| |
|
moves it to the front end of L.
|
| void |
L.move_to_rear(list_item it) |
| |
|
moves it to the rear end of L.
|
| void |
L.move_to_back(list_item it) |
| |
|
same as L.move_to_rear(it).
|
| void |
L.assign(list_item it, E x) |
| |
|
makes x the contents of item it.
Precondition it is an item in L.
|
| void |
L.conc(list<E>& L1, int dir = LEDA::after) |
| |
|
appends (
dir = LEDA : : after or prepends
(dir = LEDA::before) list L1 to list L and
makes L1 the empty list.
Precondition: L! = L1
|
| void |
L.swap(list<E>& L1) |
swaps lists of items of L and L1;
|
| void |
L.split(list_item it, list<E>& L1, list<E>& L2) |
| |
|
splits L at item it into lists L1 and L2. More precisely,
if it! = nil and
L = x1,..., xk - 1, it, xk + 1,..., xn
then
L1 = x1,..., xk - 1 and
L2 = it, xk + 1,..., xn. If
it = nil then L1 is made empty and L2 a copy of L. Finally
L is made empty if it is not identical to L1 or L2.
Precondition it is an item of L or nil.
|
| void |
L.split(list_item it, list<E>& L1, list<E>& L2, int dir) |
| |
|
splits L at item it into lists L1 and L2. Item it
becomes the first item of L2 if dir==LEDA::before and the
last item of L1 if dir=LEDA::after.
Precondition it is an item of L.
|
| void |
L.apply(void (*f)(E& x)) |
for all items < x > in L function f is
called with argument x (passed by reference).
|
| void |
L.reverse_items() |
reverses the sequence of items of L.
|
| void |
L.reverse_items(list_item it1, list_item it2) |
| |
|
reverses the sub-sequence
it1,..., it2 of items of L.
Precondition it1 = it2 or it1 appears before it2 in L.
|
| void |
L.reverse() |
reverses the sequence of entries of L.
|
| void |
L.reverse(list_item it1, list_item it2) |
| |
|
reverses the sequence of entries
L[it1]...L[it2].
|
| void |
L.permute() |
randomly permutes the items of L.
|
| void |
L.permute(list_item* I) |
permutes the items of L into the same order as stored in the
array I.
|
| void |
L.clear() |
makes L the empty list.
|
| void |
L.sort(int (*cmp)(E, E ), int dd=1) |
| |
|
sorts the items of L using the ordering defined
by the compare function
cmp : E x E 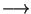 int,
with int,
with
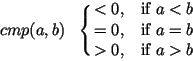
More precisely, if
(in1,..., inn) and
(out1,..., outn) denote the values of L
before and after the call of sort, then
cmp(L[outj], L[outj + 1]) < = 0 for
1 < = j < n and there is a
permutation
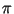 of [1..n] such that
outi = in of [1..n] such that
outi = in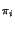 for
1 < = i < = n
. for
1 < = i < = n
.
|
| void |
L.sort() |
sorts the items of L using the default ordering of type E,
i.e., the linear order defined by function
int compare
(const E&, const E&).
|
| void |
L.merge_sort(int (*cmp)(E, E )) |
| |
|
sorts the items of L using merge sort and the ordering
defined by cmp. The sort is stable, i.e., if x = y and
< x > is before < y > in L then < x > is before
< y > after the sort. L.merge_sort() is more efficient
than L.sort() if L contains large pre-sorted intervals.
|
| void |
L.merge_sort() |
as above, but uses the default ordering of type E.
|
| void |
L.bucket_sort(int i, int j, int (*f)(E )) |
| |
|
sorts the items of L using bucket sort,
where
f : E 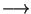 int with
f (x) int with
f (x) 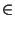 [i..j] for
all elements x of L. The sort is stable,
i.e., if f (x) = f (y) and < x > is before < y > in
L then < x > is before < y > after the sort. [i..j] for
all elements x of L. The sort is stable,
i.e., if f (x) = f (y) and < x > is before < y > in
L then < x > is before < y > after the sort.
|
| void |
L.bucket_sort(int (*f)(E )) |
| |
|
same as bucket_sort(i,j,f) where i and j are the
minimal and maximal value of f(e) as e ranges over
all elements of L.
|
| void |
L.merge(list<E>& L1, int (*cmp)(E, E )) |
| |
|
merges the items of L and L1 using the ordering defined by
cmp. The result is assigned to L and L1 is made empty.
Precondition L and L1 are sorted incresingly according to the
linear order defined by cmp.
|
| void |
L.merge(list<E>& L1) |
merges the items of L and L1 using the default linear
order of type E.
|
| void |
L.unique(int (*cmp)(E, E )) |
| |
|
removes duplicates from L.
Precondition L is sorted incresingly according to the ordering
defined by cmp.
|
| void |
L.unique() |
removes duplicates from L.
Precondition L is sorted incresingly according to the default
ordering of type E.
|
| list_item |
L.search(E x) |
returns the first item of L that contains x,
nil if x is not an element of L.
Precondition compare has to be defined for type E.
|
| list_item |
L.min(int (*cmp)(E, E )) |
returns the item with the minimal contents with respect
to the linear order defined by compare function cmp.
|
| list_item |
L.min() |
returns the item with the minimal contents with respect
to the default linear order of type E.
|
| list_item |
L.max(int (*cmp)(E, E )) |
returns the item with the maximal contents with respect
to the linear order defined by compare function cmp.
|
| list_item |
L.max() |
returns the item with the maximal contents with respect
to the default linear order of type E.
|
| void |
L.read(istream& I, char delim = (char)EOF) |
| |
|
reads a sequence of objects of type E terminated
by the delimiter delim from the input stream I
using operator>>(istream&,E&).
L is made a list of appropriate length and the
sequence is stored in L.
|
| void |
L.read(char delim = '
\n') |
calls L.read(cin, delim) to read L from
the standard input stream cin.
|
| void |
L.read(string s, char delim = '
\n') |
| |
|
As above, but uses string s as a prompt.
|
| void |
L.print(ostream& O, char space = ' ') |
| |
|
prints the contents of list L to the output
tream O using operator<<(ostream&,const E&)
to print each element. The elements are separated by
character space.
|
| void |
L.print(char space = ' ') |
calls L.print(cout, space) to print L on
the standard output stream cout.
|
| void |
L.print(string s, char space = ' ') |
| |
|
As above, but uses string s as a header.
|
| list<E>& |
L = L1 |
The assignment operator makes L a copy of
list L1. More precisely if L1 is the sequence
of items
x1, x2,..., xn then L is made a
sequence of items
y1, y2,..., yn with
L[yi] = L1[xi] for
1 < = i < = n.
|
| E& |
L[list_item it] |
returns a reference to the contents of it.
|
| list_item |
L[int i] |
an abbreviation for L.get_item(i).
|
| list_item |
L += E x |
same as L.append(x); returns the new item.
|
| ostream& |
ostream& out << L |
same as L.print(out); returns out.
|
| istream& |
istream& in >> list<E>& L |
same as L.read(in)); returns in.
|
The data type list is realized by doubly linked linear lists. All operations
take constant time except for the following operations: search and rank take
linear time O(n), item(i) takes time O(i), bucket_sort takes time
O(n + j - i) and sort takes time
O(n*c*log n) where c is the
time complexity of the compare function. n is always the current length of
the list.
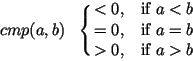
![]() of [1..n] such that
outi = in
of [1..n] such that
outi = in![]() for
1 < = i < = n
.
for
1 < = i < = n
.